- Sep 23, 2025
- By TJICLondon
Bursitis explained
Bursitis Explained - How to Treat Hip, Elbow, and Shoulder Bursitis Without Surgery
Bursitis may sound like a complicated medical problem, but in reality it’s a very common source of joint pain. If you’ve noticed soreness in your hip, shoulder, or elbow, bursitis could be the culprit – and the good news is that it’s often treatable without surgery.
What Is Bursitis?
Inside many of your joints are tiny fluid-filled sacs called bursae. They act as cushions, reducing friction between bones, tendons, and muscles. When one of these sacs becomes irritated or inflamed, the result is bursitis – a painful condition that can make even simple movements uncomfortable.
Symptoms of Bursitis
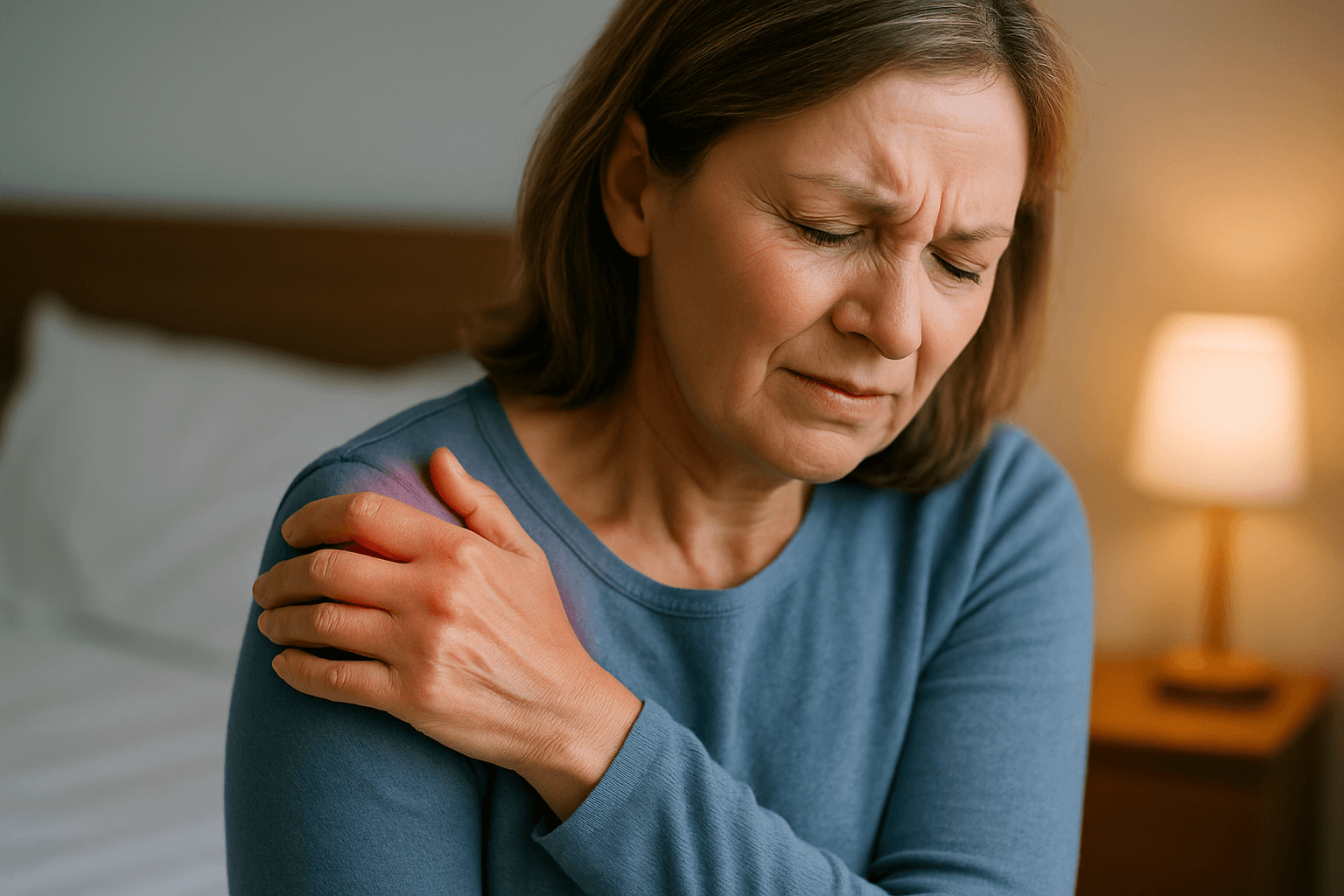
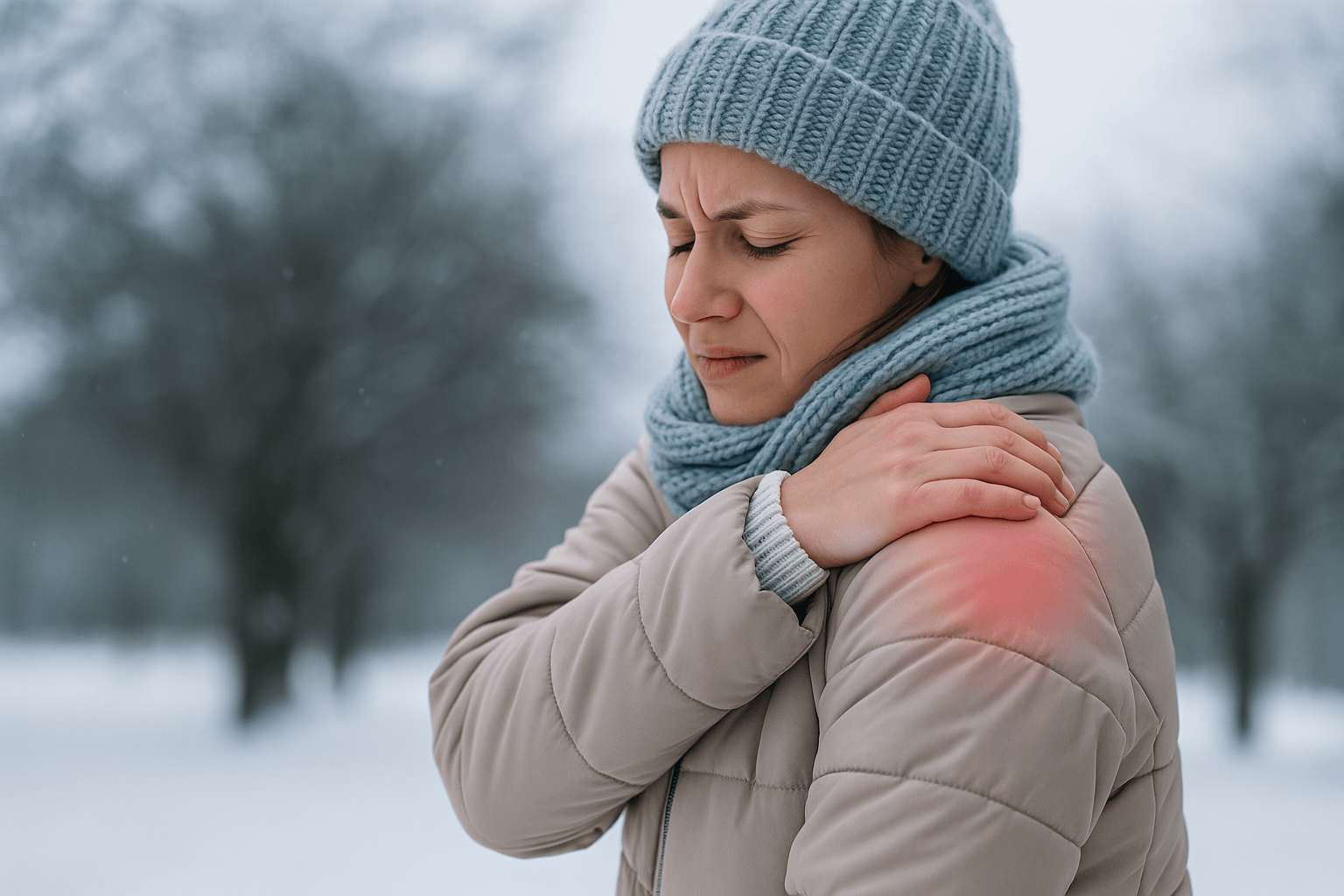
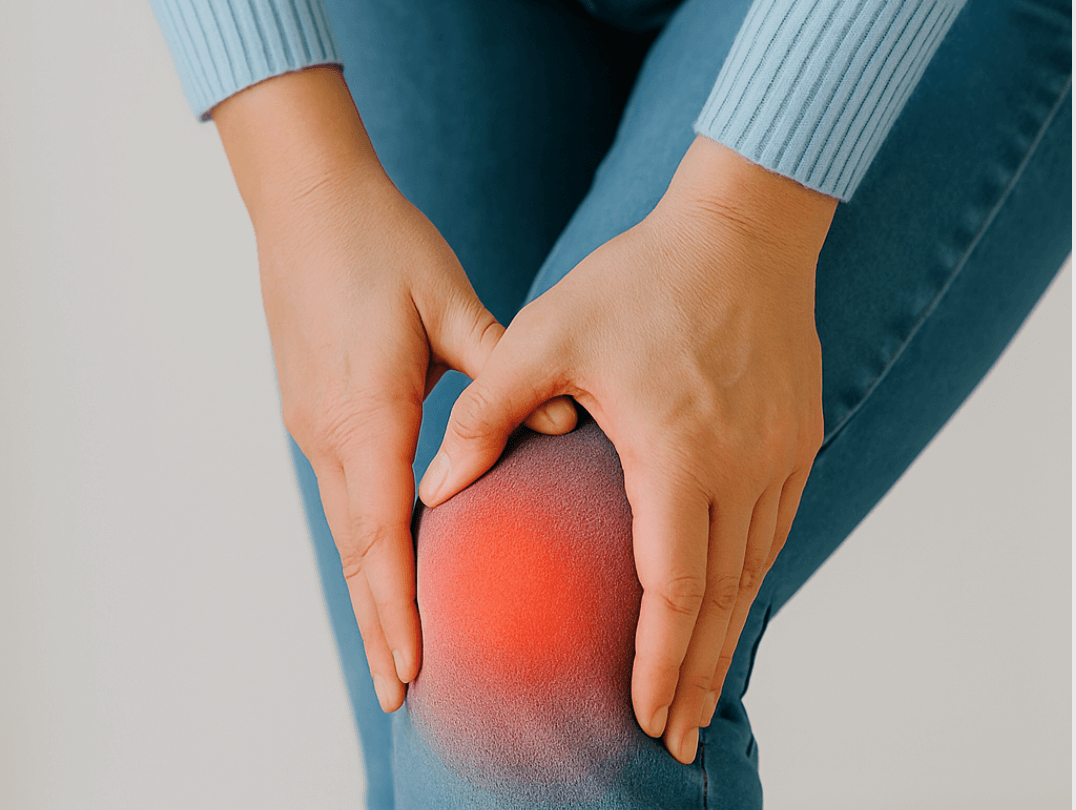
The most common sign of bursitis is pain over the affected joint, usually felt as a dull ache that gets worse with movement or pressure. You may also notice swelling, warmth, or tenderness in the area. In the shoulder, bursitis can make lifting your arm difficult; in the hip, lying on your side may be painful; and in the elbow, even resting your arm on a desk can trigger discomfort.
What Causes It?
Bursitis often develops gradually due to repetitive motion. Athletes, musicians, or people with jobs involving lots of kneeling or leaning are particularly at risk. Sometimes it appears after a sudden injury or as a side effect of another condition like arthritis or gout.
Treatments That Work
For many people, bursitis improves with rest, ice, and avoiding aggravating activities. Anti-inflammatory tablets can help reduce pain in the short term. Physiotherapy may also be recommended to strengthen the muscles around the affected joint.
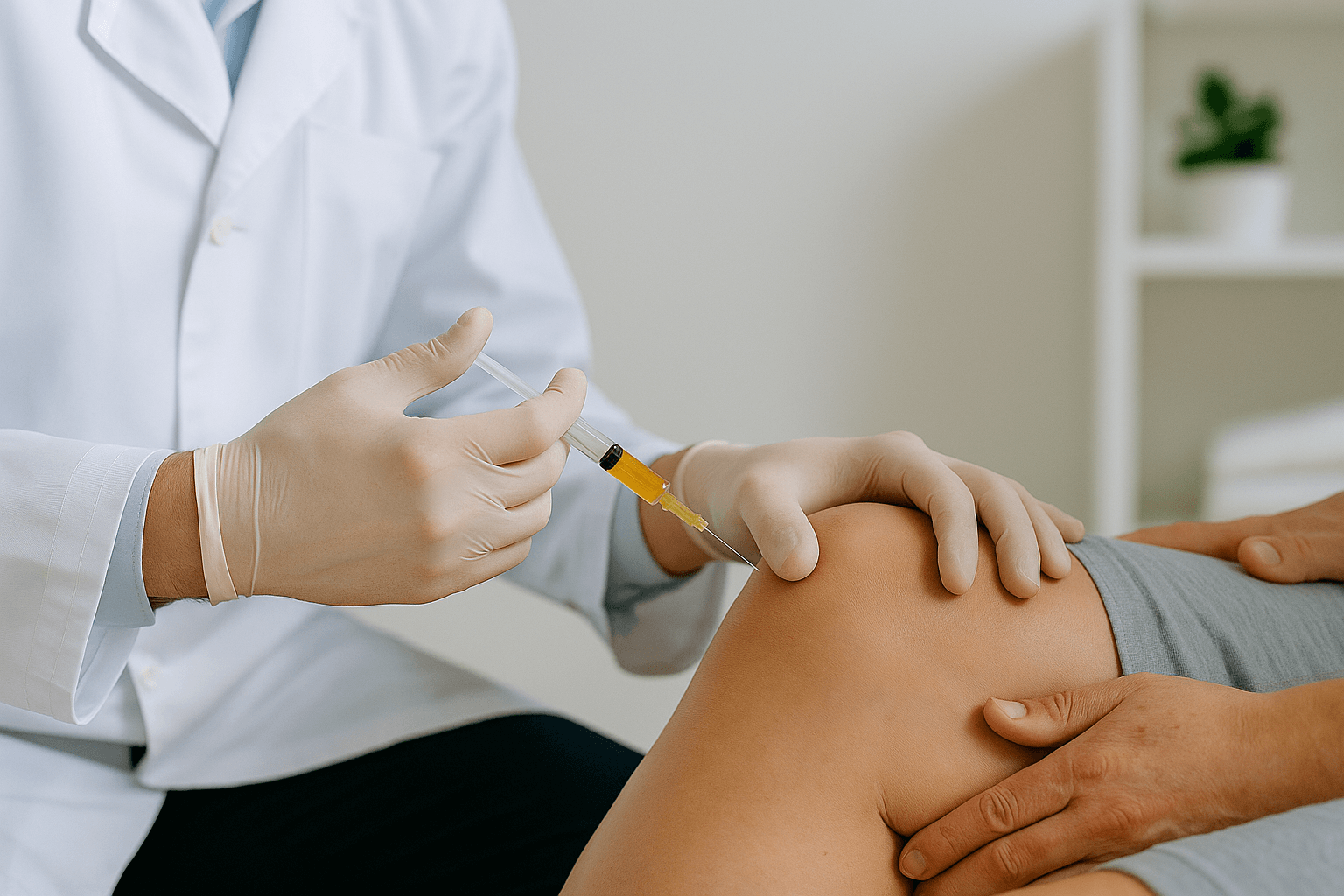
However, when symptoms don’t improve, injections can make a big difference. An ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection delivers medication directly into the inflamed bursa, calming irritation and providing relief that can last for months. Unlike surgery, injections are quick, minimally invasive, and performed in an outpatient clinic.
Surgery - Rarely Needed
Most cases of bursitis respond well to conservative treatments. Surgery is usually considered only when the condition becomes chronic and other treatments fail. Even then, the procedure is straightforward and recovery is usually good.
Key Takeaway
Bursitis can be disruptive, but with the right treatment plan you don’t have to live with ongoing pain. Injections, in particular, are an excellent option when self-care isn’t enough